Stem cell research is an emerging field that uses cells in order to treat and cure illnesses. Some of these common illnesses include spinal cord injuries and arthritis. Stem cell therapies such as platelet-rich plasma are becoming increasingly popular among patients with joint issues.
A platelet-rich plasma injection is a procedure that involves removing the patient’s blood, separating the platelets (small blood particles), and injecting them into the patient’s arthritic joints.
History of Stem Cell Research
Stem cell research has been used to treat and attempt to provide cures for many common diseases, including arthritis. The earliest recorded use of stem cells can be traced back to the year 1924 when Dr. George Klein injected ground-up tissue into a man with a disease that affected his muscle.
In 1930, Dr. Robert Adey observed that certain blood cells could multiply in the laboratory and helped scientists discover the process where blood cells become more powerful by dividing rapidly. This process is called “haploid cell division“, in which one cell becomes two.
Research into stem cells continued, and in the 1950s, Dr. C.C. Little’s work helped to develop an understanding of blood platelets and their role in clotting. Dr. Little also discovered that each blood cell only lives for a short period of time before it dies and is replaced by another young blood cell.
In 1962, Dr. William Dameshek conducted his research on embryonic tissue and discovered that muscle cells could be derived from embryonic tissue; he also found that pancreatic tissue can be generated from embryonic pancreas tissue.
In 1966, Dr. James Till had the idea that cells could become diabetes resistant if they were injected into the pancreas. Dr. Till’s research led to the creation of insulin, which is produced by beta cells in the pancreas.
In 1983, Dr. Edward Behr used a virus to insert genes into the skin. He then injected these genes into a cell and found that they could be turned on or off 22 days after being injected into the cell.
The use of stem cells began in 1989 when Dr. James Thomson discovered that he would need a donor in order to receive bone marrow transplants. He then started his own bone marrow registry and in 1991, received the first bone marrow transplant from a donor whose sperm had been used in the procedure.
In the 1990s, Dr. James Thomson found that pancreatic stem cells could be derived from stem cells taken from adult digestive tract tissue. In 1993, he encouraged scientists to focus on stem cell treatments for patients with diabetes.
By 2002, Dr. James Thomson discovered that he could use genetic engineering to control how blood cells divide by turning off one gene in every blood cell. This provides a half-time switch so that their body will remain stable until they are cured. At this point, the scientific community began to view it as possible to cure many disease processes with stem cells.
Platelet Rich Plasma Injections
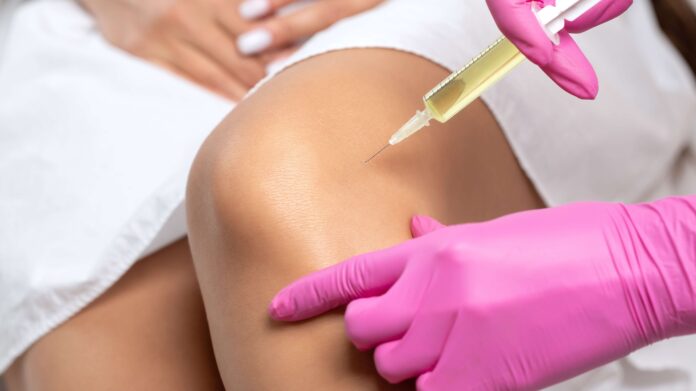
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a medical treatment that uses an individual’s own blood to be injected into their joints. It has been used since the 1950s and is most often used to treat joints in athletes. PRP injections are also used for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and tendinitis.
The procedure for this type of injection can be taken in numerous ways. PRP injections can either be done using a “single needle” or a “fluxor”. A “single needle” is designed for patients that have one joint being treated.
With a single needle, the PRP injection can also be done without numbing the area by injecting through the skin to obtain a deeper injection. A “fluxor” is used when injections are being done to multiple joints at once. Because of this, a numbing solution can be used before each blood draw to obtain a deeper blood sample needed for PRP.
On average, the procedure takes between 15-30 min and is most often done under x-ray guidance or at an outpatient treatment facility. The actual PRP injection takes less than five minutes and is most commonly performed with an ultrasound machine in order to verify the placement of the injection.
Benefits of Platelet Rich Plasma Injections
PRP injections have a high success rate, with many patients receiving long-term relief from their pain. Some of the benefits of PRP injections are:
- The procedure is minimally invasive and has no reported side effects.
- It does not require surgery and can be done in a physician’s office.
- It has been shown to be able to lessen the need for surgery over time by providing pain relief in patients whose joints are beyond repair.
- The major benefit of this procedure is that it has shown to be an alternative means for providing pain relief in people whose joints have failed them. For people who are not candidates for surgery, PRP injections can provide relief without serious side effects.
Risks of Platelet Rich Plasma Injections
The main risk associated with PRP injections is that it uses the patient’s own blood, which means that there will be blood that must be drawn for the procedure.
This can cause some bruising and soreness at the injection site as well as a possible allergic reaction to the anticoagulant medication used during the procedure. Some patients may also experience a fever due to minor infection from cytokines released by platelets, but this usually subsides within 4-5 days after treatment.
All patients should be educated about the risks and benefits of PRP injections before starting the procedure. This can help decrease the risk of complications that may arise during the procedure.
Combining PRP Injections With Physical Therapy

Physiotherapy is used to speed up recovery from injuries that result from repetitive activities. Along with physical therapy, PRP injections are also used in treating athletes who have injuries. The injections can be combined with physical therapy treatments to speed up the recovery process and relieve pain caused by injuries.
PRP Injections for Athletic Injuries
Injury can occur during sports because of overexertion or trauma such as a direct blow to the body. Sport-related injuries can range from small cuts and bruises to broken bones. When an injury occurs during sport, it is important to get treatment as soon as possible in order to accelerate the healing process and return to action as quickly as possible.
Can Stem Cell Therapy Support Joint Health?

There has been a lot of research recently into the efficacy of stem cell therapy as a treatment for damaged joints. Some studies have found that it can be helpful in treatments, although the results are somewhat mixed. What is clear though, is that despite some attempts to use stem cells as a way to regenerate tissue in damaged joints, this may not be possible or practical.
The idea behind stem cell therapy is that it might one day enable doctors to replace damaged cartilage and other important structures in joints. In theory, this could revolutionize the treatment of conditions such as arthritis.
However, the available data is not yet sufficient to support this claim. Some studies have concluded that stem cells may be able to help some patients. However, many of these studies were too small and used different cell types to make these conclusions, so it is unclear whether stem cell therapy can ever produce positive results without large-scale clinical trials.
As of now, it appears that stem cell therapy may only be able to help certain people with damaged joints. Further research is needed to determine if this can ever be a viable treatment option for joint diseases such as arthritis.
Conclusion
PRP injections are a pain reliever that can be used to treat many different types of injuries. They have been shown to be an effective treatment for athletes, who often need pain relief that does not come from medication. PRP injections can help speed up the recovery process by providing relief within a short period of time.